Parents should not get mislead by Symptoms of Tonsillitis in their Children as COVID
Parents are concerned that the symptoms of tonsillitis, which are more common in children, are more likely to coincide with the symptoms of chickenpox, which is being traded around the world. Tonsillitis is more common in children, especially from the onset of the rainy season until the end of winter, but the same symptoms are also associated with Covid disease, making it difficult for them to provide proper treatment to children. That is why children can become aware of the differences between the symptoms of Covid disease and the symptoms of tonsillitis and try to get the right treatment.
Affect of Tonsillitis –
The World Health Organization estimates that 600 million children worldwide are infected with tonsillitis. At the same time, it is estimated that 20 to 30 million children in India are infected and more than 2 lakh children have their tonsils surgically removed. However, experts say that the number may be even higher, depending on the symptoms of the disease, which are contagious, given the Indian census that more than 35 per cent of the population are children. According to a survey conducted in 2015, every child under the age of 15 is affected by the disease in about 7 cases.
Symptoms are especially common in children between the ages of 5 and 15 years. As a result, children often suffer from poor growth, weight gain, insomnia or trouble sleeping, and fever. As a result, the education of the children is disrupted and their talents in education are not shown and they are left behind. In addition to the frequent exposure to the disease, the medical expenses associated with it can cause financial burdens on the family as well as other problems. In this context it is very important to control the disease completely by providing proper treatment at the right time.
What is tonsillitis?
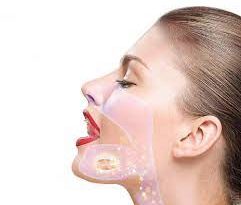
The lymph nodes on either side of our throat are called tonsils. These tonsils are the first defense system that prevents infections caused by bacteria or viruses that enter our body through the mouth. However, in an attempt to prevent such diseases, the tonsils often become infected with these viruses or bacteria, leading to tonsillitis. Tonsillitis can affect any person but is a common problem in children. It is most common in children between the ages of 5 and 15 years. The main symptoms of this disease are sore throat, inflammation along with swollen tonsils and high fever.
However, the disease, which is caused by a variety of viruses and bacteria, can be transmitted from one child to another. Especially in diseases caused by streptococcal bacteria the throat can become swollen and dangerous if not treated properly. The disease can be easily diagnosed. In addition, under normal circumstances, the symptoms of the disease subside within 7 days.
There are three main types of tonsillitis: Acute, Chronic and Recurrent. However, if the symptoms do not subside within 7 days, it can be considered as acute tonsillitis. However, if the symptoms do not go away within 10 days, it should be treated as a chronic disease. However, recurrent tonsillitis should be considered if the disease recurs frequently in children despite treatment.
Symptoms of tonsillitis
Symptoms include sore throat or inflammation, difficulty swallowing, hoarseness, bad breath, fever over 101, neck stiffness, and loss of appetite. Depending on the duration of these symptoms, the severity of the disease should be considered normal or acute or chronic.
In some children, tonsillitis may be due to diphtheria or some other illness.
When to consult a doctor
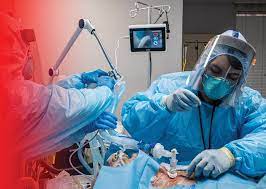
If the fever persists for two to three days with the appearance of the above symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. Doctors prescribe treatment depending on the severity of the disease and the history of the disease in children. However, in cases where the disease is acute or chronic, the doctor may prescribe or require removal of the tonsils through an operation called tonsillectomy.
However, with modern medical techniques, the surgery can be done in a procedure called cobblestone without losing much blood, so you can go home from the hospital in just 8 hours after the surgery is completed.
Especially children between the ages of 5 and 15 are playing at home or at school, in playgrounds or on the roads. It seems to us that during these games they put their hands in the mud and tumbling as part of the game, so bacteria or viruses in those areas are more likely to enter the mouth after being attached to the hands. So we often notice that they are infected with some kind of bacteria or virus.